How Are the Alveoli Designed to Maximize the Exchange of Gases
Hello friends, welcome to MuskanTutor Education is our topic today. Exchange of Gases and Student Questions How are alveoli designed to maximize the exchange of gases. And how are the alveoli designed to maximize the exchange of gases class 10? So through air, we absorb many gases into our body. But the important gases are those which perform functions in our body. And that is oxygen and carbon dioxide from our bodies. And the remaining gases, nitrogen, and hydrogen, come out of our body.
Exchange of Gases in the Lungs
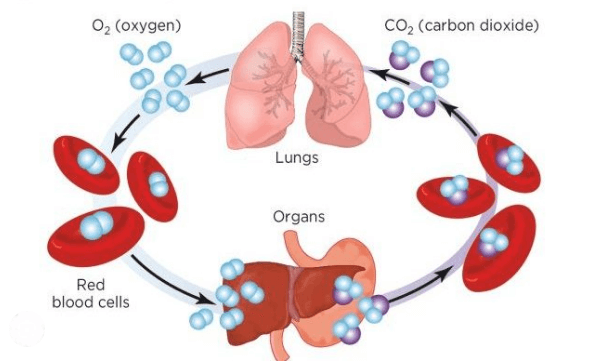
That is, gaseous exchange in the lungs means the exchange of gases in the lungs. This means that oxygen goes to the tissues and carbon dioxide comes out of the tissues and comes to the lungs. And then it is expelled from the lungs through the nose. This means that oxygen reaches each cell and carbon dioxide goes out of the body through the cells. This is a gaseous exchange or exchange of gases in the lungs.

So how does the exchange of gases take place in the lungs? Before knowing this, you people should see this picture of lungs. The small parts you see in it are called air sacs. In science, these are called Alveoli.
So I have shown one alveolus in a larger size. There is a network of blood cells spread in it. Blood cells means blood has thin veins and tubes. These are called blood cells. So, there are approximately 15 crore cells in one lung of a human being. That is, the alveoli which are air sacs, there are approximately 15 crore air sacs in one lung. About 30 crore air sacs are found in both the lungs together. The exchange of gases takes place through these air sacs. So let us now tell you how the exchange of gases takes place through them.
So the air taken in during inhalation fills the air sacs of the lungs. There is a dense network of blood cells in the wall of the alveoli. Here we tell you that inhalation or exhalation means when we inhale. That is, the inhaled air fills the air sacs of the lungs. A dense network of blood cells is spread in the thin wall of the alveoli of both our lungs. That means there is a dense network of blood cells inside the cells.
The wall of this air sac is very thin and made of epithelium. That is, the walls of the air sacs are made of thin and smooth epithelium. The walls of the alveoli and blood cells are permeable to oxygen and carbon dioxide. Gas exchange occurs by simple normal diffusion. Oxygen goes from the alveoli to the blood cells and carbon dioxide from the blood cells goes to the alveolar cells.
You should know that apart from oxygen, there are many other gases found in the air. Nitrogen is about 78%, oxygen is about 20%, carbon dioxide is about 0.04% and water vapor is about 0.5%. Apart from this, gases like helium, argon, neon, etc. are also found in small quantities in the air.
Transport of Oxygen from Lungs to Tissue
When oxygen reaches the blood cells and reacts with the hemoglobin of RBCs. So oxyhemoglobin is formed. So let us tell you that three types of corpuscles are found in our blood. First, red blood cells, second, white blood cells and blood platelets or RBC, WBC, and thermosets.
The red blood cells in our blood which are RBCs contain hemoglobin which transports oxygen, then the oxygen reaches the blood cells and forms oxyhemoglobin from the RBCs. The temporary compound oxyhemoglobin reaches cells and tissues and releases oxygen. Oxidizes glucose from free and O2 foods. As a result, CO2 and H2O occur and energy is released.
Hb + 4O2 → Hb(O2)4
Hemoglobin + Oxygen = Oxyhemoglobin
How Is Oxyhemoglobin Disintegrated?
CO2 is formed from the metabolism of glucose and other substances in tissue cells. And oxygen gets used. As a result of this, the concentration of oxygen in tissue fluids and cells is always lower than in blood. Whereas the concentration of CO2 is higher. If the concentration of oxygen is low and the concentration of CO2 is high, then oxyhemoglobin disintegrates in areas with low concentrations of oxygen. The oxygen is released and now diffuses from the blood cells into the tissue fluid. And from there, it reaches every cell. In this way, oxygen gets decomposed.
How Is Co2 Transported from Tissue to Lung?
The CO2 produced as a result of cellular absorption diffuses from the tissue cells and reaches the tissue fluid. And from there the blood enters the cells. About 5 to 10 percent of CO2 reaches the lungs in the form of organic acids, 80 to 85 percent of CO2 in the form of sodium and potassium bicarbonate, and about 10 percent in the form of carboxyhemoglobin. Through normal diffusion, CO2 moves from the blood cells to the lungs. And thus the exchange of O2 and CO2 continues. This means that gas keeps flowing in the lungs.
CO2 + H2O⟶H2CO3
How Are the Alveoli Designed to Maximize the Exchange of Gases Class 10th
So let us know the short answer and summary of Class 10th Science question how are the alveoli designed to maximize the exchange of gases. So how are alveoli designed to exchange gases? So the alveoli provide a surface once. So that gas can be exchanged. A network of blood vessels is present. There is a network of blood cells in the wall of the alveoli.
When you breathe, your ribs get lifted. And which is the diaphragm. It becomes flat so space is created in the chest cavity. For example, when the ribs grow, they become slightly lifted. Due to this and the flatness of the diaphragm, space is created in the chest cavity.
And due to this, the air that we breathe gets sucked inside the lungs and alveoli. Now because there is oxygen, when we are breathing, we are breathing. It comes into the blood and the carbon dioxide goes into the body. And goes back through the body into the air through the hostess. So this is how oxygen and carbon dioxide are exchanged.

The answer to How are the alveoli designed to maximize the exchange of gases class 10 is written in the image above. You can remember the answer from the images and in the article. I wrote for you the alveoli designed to maximize the exchange of gases summery. It is written to make you understand. This is a summary of sorts. You can easily understand the details and summary given in it. And when you are remembering the answer from the image then read the article before memorizing, it will help you a lot.
Conclusion
Friends, I hope that you have read this article and you have understood this article. And you have understood that the answer to your inquiry how are the alveoli designed to maximize the exchange of gases class 10th is very important. According to the question of your exam. These questions are definitely asked in your exam, so please memorize their answers. By memorizing the answer line, you will pass the exam with good marks.